3 Main Types Of Protists
Table of Contents
- What are Protists?
- Characteristics of Kingdom Protista
- Classification of Protista
What are Protists?
Protists are simple eukaryotic organisms that are neither plants nor animals or fungi. Protists are unicellular in nature but tin besides be found as a colony of cells. Most protists alive in water, clammy terrestrial environments or even as parasites.
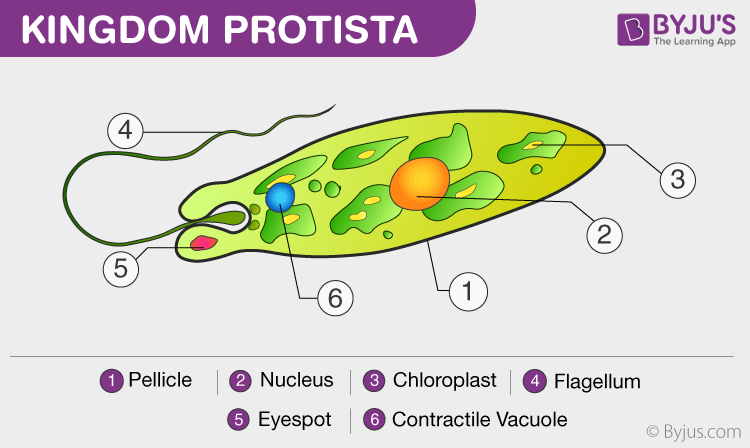
Euglena, a eukaryotic protist
The term 'Protista' is derived from the Greek word "protistos", meaning "the very first". These organisms are usually unicellular and the cell of these organisms contains a nucleus which is bound to the organelles. Some of them fifty-fifty possess structures that aid locomotion like flagella or cilia.
Scientists speculate that protists form a link between plants, animals and fungi as these three kingdoms diverged from a common protist-similar antecedent, billions of years ago. Though this "protists-similar" antecedent is a hypothetical organism, we can trace some genes constitute in modern animals and plants to these ancient organisms.
Therefore, these organisms are traditionally considered the first eukaryotic forms of life and a predecessor to plants, animals and fungi.
Detailed Insight: Eukaryotic Cells
Characteristics of Kingdom Protista
The principal feature of all protists is that they are eukaryotic organisms. This means that they take a membrane-enclosed nucleus. Other characteristic features of Kingdom Protista are as follows:
- These are usually aquatic, nowadays in the soil or in areas with wet.
- About protist species are unicellular organisms, however, there are a few multicellular protists such as kelp. Some species of kelp grow and then large that they exceed over 100 feet in peak. (Behemothic Kelp).
- Just like whatsoever other eukaryote, the cells of these species take a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
- They may exist autotrophic or heterotrophic in nature. An autotrophic organism tin can create its own food and survive. A heterotrophic organism, on the other hand, has to derive nutrition from other organisms such equally plants or animals to survive.
- Symbiosis is observed in the members of this class. For instance, kelp (seaweed) is a multicellular protist that provides otters, protection from predators amidst its thick kelp. In turn, the otters swallow sea urchins that tend to feed on kelp.
- Parasitism is also observed in protists. Species such as Trypanosoma protozoa tin cause sleeping sickness in humans.
- Protists showroom locomotion through cilia and flagella. A few organisms belonging to the kingdom Protista have pseudopodia that assist them to move.
- Protista reproduces past asexual means. The sexual method of reproduction is extremely rare and occurs only during times of stress.
Read more than: Kingdom Protista
Nomenclature of Protista
Kingdom Protista is classified into the following:
Protozoa
Protozoans are unicellular organisms. Historically, protozoans were chosen "fauna" protists equally they are heterotrophic and showed animal-like behaviours.
There are also parasitic protozoans which live in the cells of larger organisms. Virtually of the members do not accept a predefined shape. For example, an amoeba tin change its shape indefinitely just a paramecium has a definite slipper-like shape. The most well-known examples of protozoans are amoeba, paramecium, and euglena. Unlike other members of this group, euglena is a free-living protozoan that has chlorophyll, which means it can make its own food.
The protozoans can be divided into four major groups:
- Amoeboid protozoans –Generally found in water bodies, either fresh or saline. They have pseudopodia (false feet) which help to change their shape and to capture and engulf food. E.g. Amoeba.
- Flagellated protozoans –As the name suggests, the members of this group take flagella. They can be free-living as well equally parasitic. E.k. Euglena.
- Ciliated protozoans –They have cilia all over their body which assistance in locomotion as well as diet. They are always aquatic. E.g. Paramecium.
- Sporozoans – These organisms are so-called because their life bicycle has a spore-like stage. For instance, the malarial parasite, Plasmodium.
Slime Moulds
Slime moulds are saprophytic organisms (they feed on dead and decaying thing). These are tiny organisms that accept many nuclei.
Usually, Slime moulds are characterized by the presence of aggregates chosen plasmodium and are even visible to the naked eye.
Read more than: Slime moulds
Chrysophytes, Dinoflagellates and Euglenoids
These form another category nether kingdom Protista. These are generally unmarried-celled or multicellular organisms. These are photosynthetic, found mostly in freshwater sources or marine lakes. They are characterized by a stiff cell wall.
Instance of chrysophytes include diatoms and gilded algae. They are characterised by the presence of a difficult siliceous cell wall. Diatomaceous world is formed due to the aggregating of jail cell wall deposits. They are photosynthetic organisms.
Dinoflagellates are photosynthetic and found in various dissimilar colours, according to the paint present in them. They show bioluminescence and known to cause red tide.
Euglenoids are the link betwixt plants and animals. They lack a cell wall but perform photosynthesis. In the absence of sunlight, they human activity as a heterotroph and feed on pocket-size organisms. The outer body roofing is a protein-rich layer known equally a pellicle. E.grand. Euglena, Trachelomonas, etc.
Read more: Algae
Economic Importance of Protists
- Protists serve as the foundation of the food concatenation.
- Protists are symbionts – having a close relationship between 2 species in which, one is benefited.
- Some protists also produce oxygen and may be used to produce biofuel.
- Protists are the chief sources of food for many animals.
- In some rare cases, Protists are harvested by humans for food and other industrial applications.
- Phytoplankton is one of the sole nutrient sources for whales
- Seaweed is an alga, which is considered a plant-similar protist.
- Zooplankton is fed on by various sea creatures including shrimp and larval crabs.
Topics That May Interest You:
- Five kingdom classification system
- Endospores
- Mass Extinctions
For more detailed information on kingdom Protista, or any other related topics, please explore BYJU'S Biology.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are Protists?
Protists include a vast drove of single-celled and multicellular organisms that have a nucleus. They besides possess highly specialized cellular machinery chosen cell organelles that aid in performing diverse life processes. Most protists are gratis-living autotrophs (such as algae) while others are heterotrophic (Amoeba) or fifty-fifty parasitic (Trypanosoma protozoa).
State a few examples of Protists.
Amoeba, Paramecium, Euglena Plasmodium, etc.
How are Protists classified?
Protists are broadly classified into 5 subdivisions based on their general characteristic features. They are classified as:
- Chrysophytes
- Dinoflagellates
- Euglenoids
- Slime moulds
- Protozoans
Outline the characteristics of Kingdom Protista.
- All protists are eukaryotic organisms. This ways that they accept a membrane-enclosed nucleus and other prison cell organelles.
- Most protists are aquatic, others are found in moist and damp environments.
- Well-nigh are unicellular, however, there are a few multicellular protists such as the giant kelp.
- They may be autotrophic or heterotrophic in nature.
- Parasitism is too observed in some protists.
- Others exhibit symbiosis.
Are all Protists unicellular?
No, non all Protists are unicellular. Protists such as moulds and algae are multicellular, i.e., they are made up of more than one prison cell. Amoeba, paramecium and euglena are unicellular organisms belonging to kingdom Protista.
3 Main Types Of Protists,
Source: https://byjus.com/biology/protista/
Posted by: cliffordponeely.blogspot.com


0 Response to "3 Main Types Of Protists"
Post a Comment